Geography of Cyprus
Between the three continents
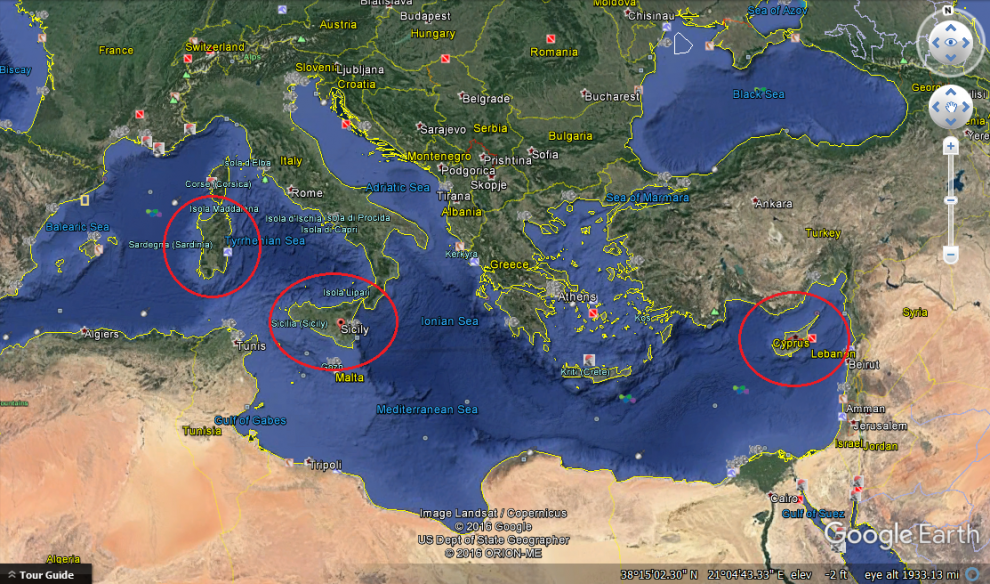
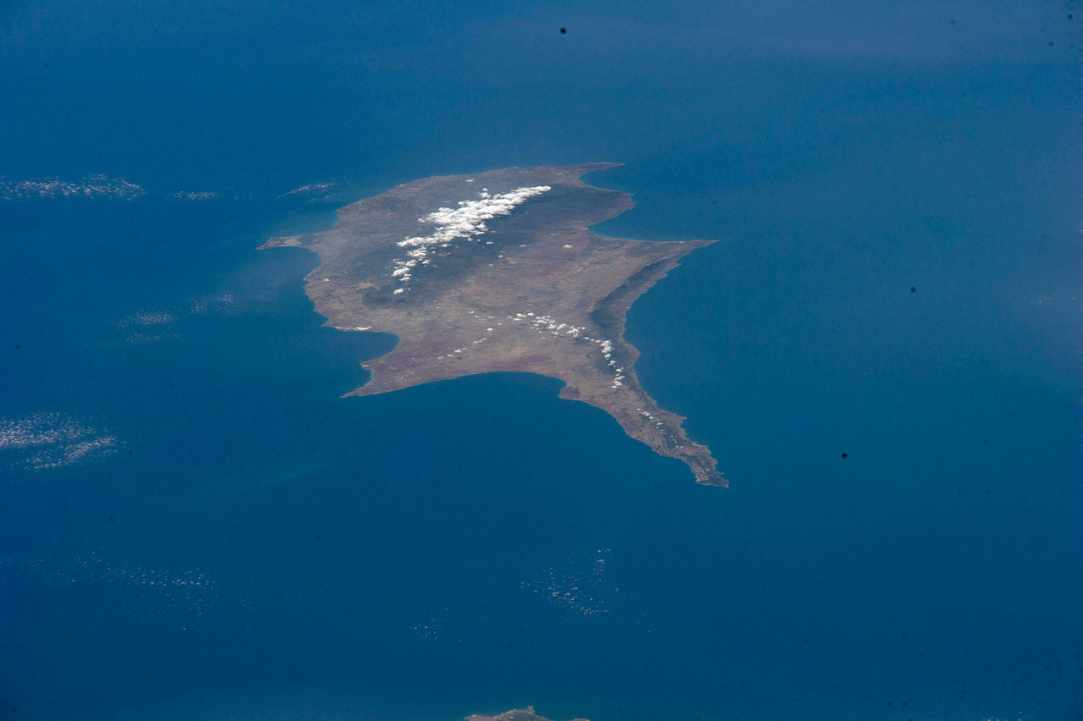
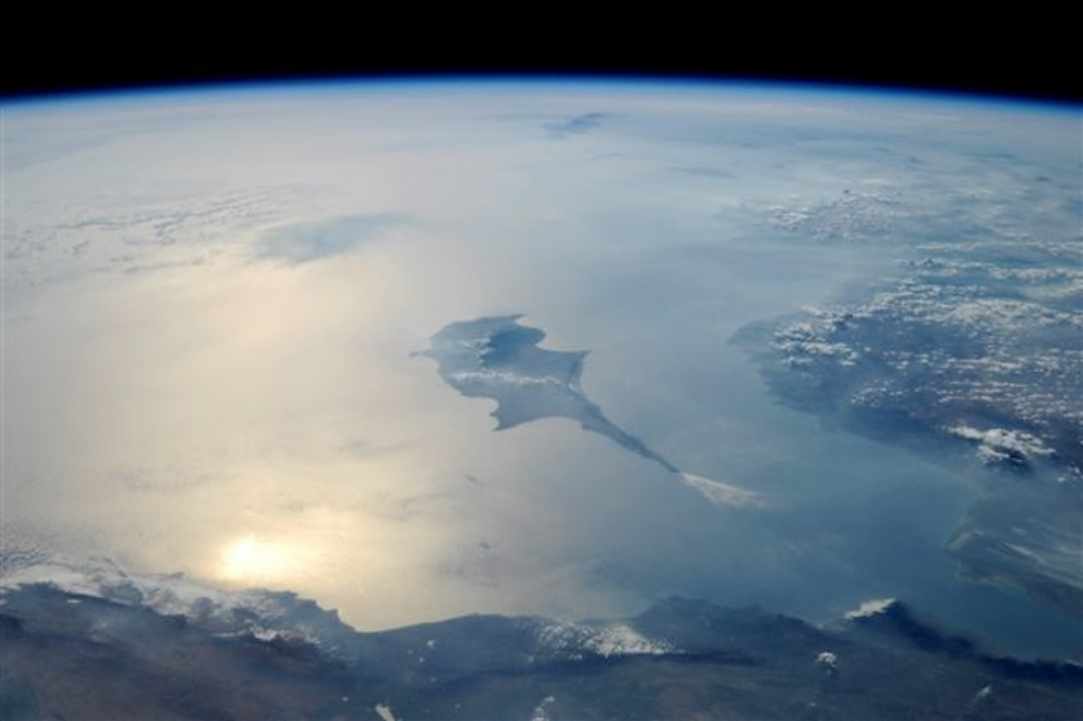
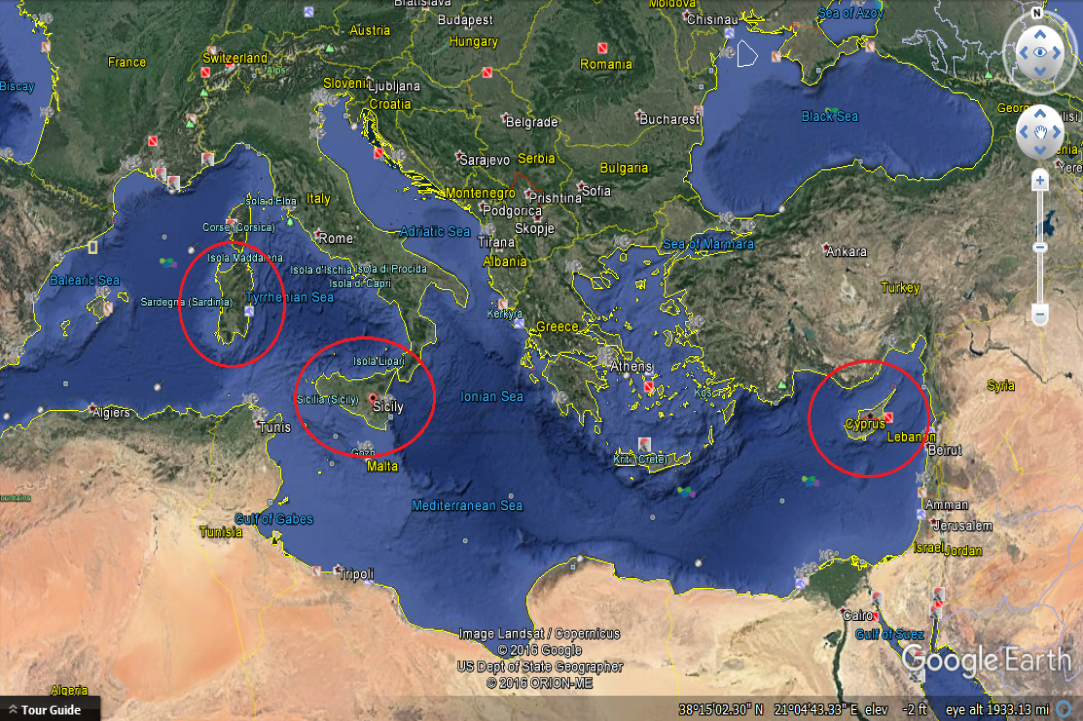
Cyprus is the third island in size of the Mediterranean sea, after Sicily and Sardinia, with an area of 9,251 km2. and total population of 858,000 (estimate in 2013) of Repuplic of Cyprus, located at the northeastern extreme point of the Mediterranean sea, between Europe, Asia and the Africa. Is the most rich in forests of the Mediterranean island.
The island of Cyprus was always part of Europe and today is a full member of the European Union, however geographically is in Asia and in the space of the eastern Mediterranean. Geopolitically, the island is divided into four segments. The Republic of Cyprus, the internationally recognized government, has legally the southern part of the island. The Turkish Republic of Northern Cyprus, diplomatically recognized only by Turkey, occupies the northern part of the island illegaly. The United Nations controlled Green Line is a buffer zone that separates the two. Lastly, two bases under British sovereignty, Akrotiri and Dhekelia, are located in the south of the island.
Cyprus is geographically divided into six districts: Nicosia, Limassol, Larnaca, Paphos, Famagusta and Kyrenia. The last two, except for a small section of Famagusta, and some areas of Nicosia, occupied by Turkish troops since 1974. The capital of the island is Nicosia. Limassol is the second largest city and Limassol municipality is the most densely populated of Cyprus. The temporary capital of the free Famagusta area is the town of Paralimni.
Cyprus has many forests, more than all of the Meditterenian islands.

In ancient times Cyprus was a pole of attraction, the center between three continents for thousand years, it was important for its geographical position and for the exploitation of the natural wealth from its neighbors. That's why Cyprus began developing a special relationship with them, through the sea route which developed active trade. For three thousand years Cyprus was the copper production center from which is why it took the name from it.
Indeed, Cyprus had been called many names. Some of these names were actually the name of the island before it became Cyprus.
Also the Eteocypriots, was the first perfumers in the Mediterranean. The perfumery that was discovered in Limassol is the oldest in the world.
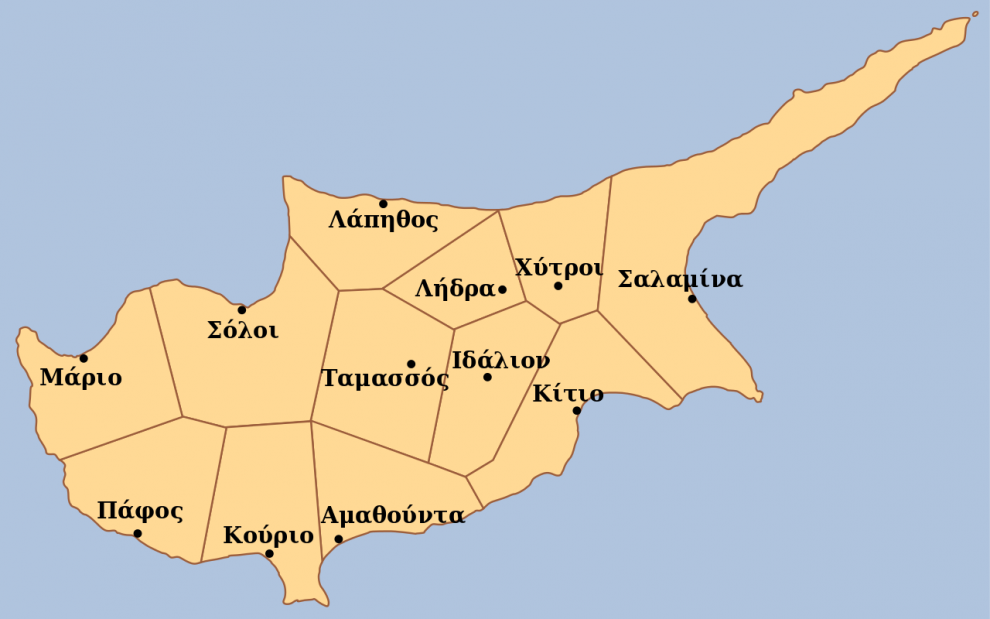
Strabo reported sixteen Cyprus beaches and towns and townships as follows:
Lapithos, Karpas, Salamis, Arsinoe, Lefkolla, Kition, Amathus, Kourion Palaipaphos, Marion, Ierokipis, Paphos, solo, Limenia, Tamassou.
Within the island there were more small old ancient cities that were the Chitre, Ledra, Idalion, Assini, Thimes and Golgoi according to Skillax.
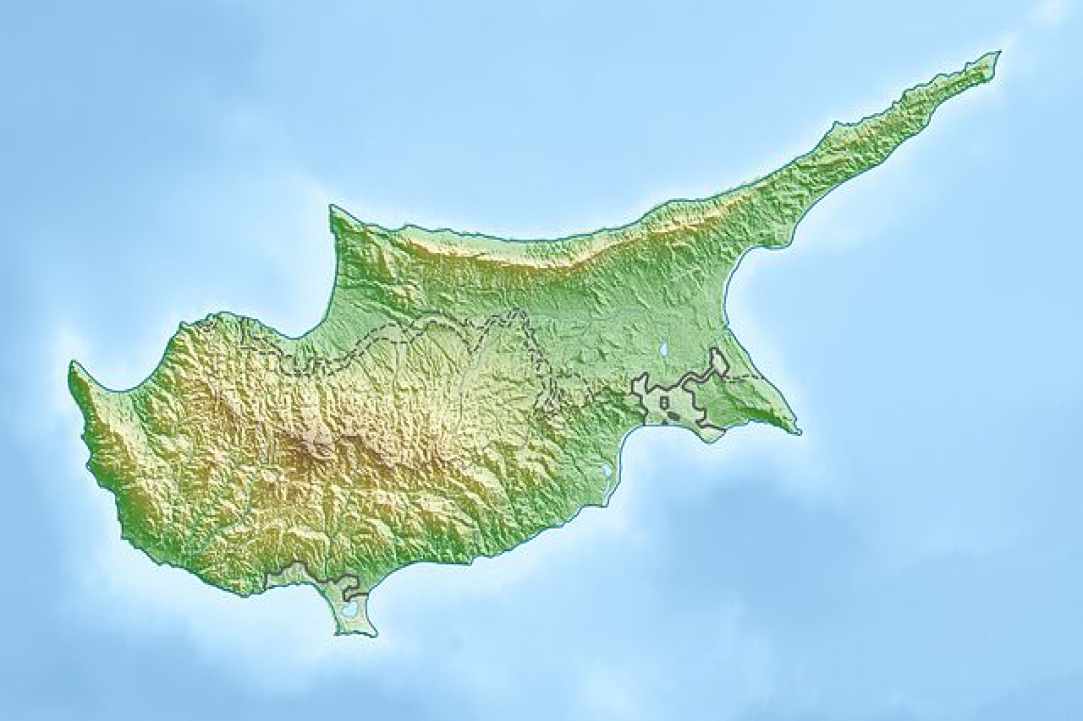
Once, Cyprus was under the sea, it is a unique worldwide fully preserved and integrated piece of oceanic crust located above the sea. Cyprus emerged from the sea two times. The first time that Troodos emerged was before 90 million years (the humans appearance was 2 million years ago). Before 70 million. years the two plates, on the border of which is the Cyprus (African and Eurasian) began to removed from each other, gaps created between them and before 25 million years the land was covered by the sea and just before 12 million years it reappeared, which was mainly the area of Troodos with another neighbor second islet, the Pentadaktylos.
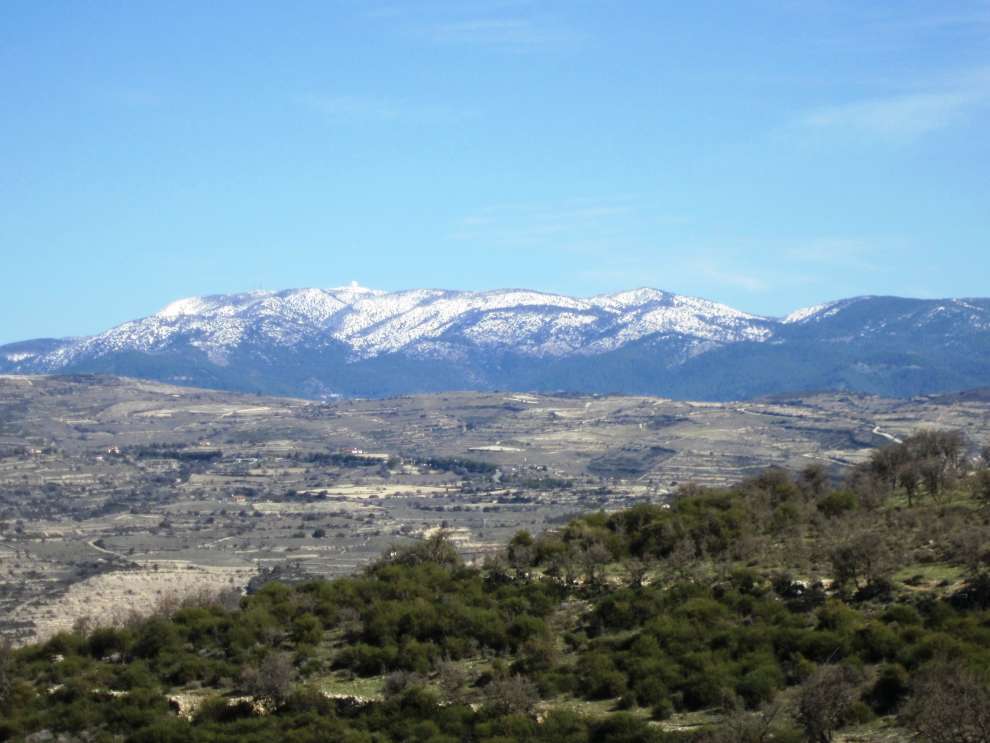
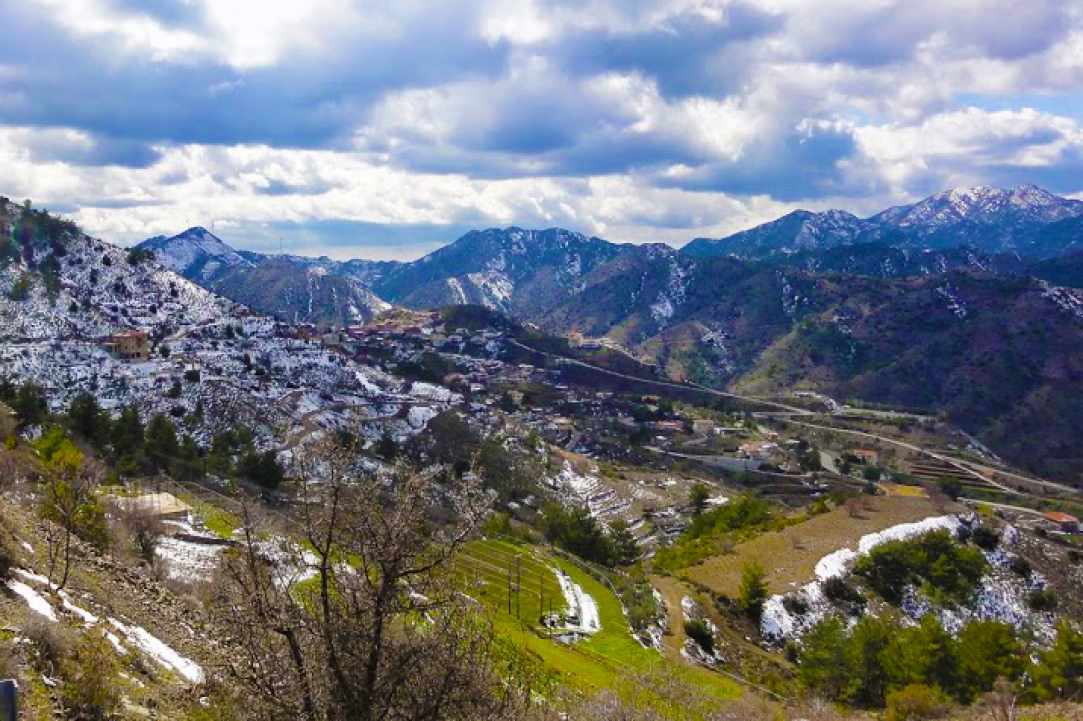
The two main mountain ranges of the island is Pentadaktylos (1023 m) and the Olympus top Troodos (or Chionistra), which has a height of 1951 m. Between the ranges lies the Mesaoria plain and the eastern part of the island is represented by the close Karpas peninsula.
Troodos, the main mountain range in Cyprus, according to scientific measurements, grows taller every year some centimeters! Many scientists from around the world study the Troodos and draw conclusions about the birth of the crust of the earth!First allegedly closely involved with the geography of Cyprus were the ancient Greeks. Strabo (63 BC-23 AD) and Claudius Ptolemy (127-151 AD), who are the first cartographers of Cyprus.
Therefore according to the Homeric legend Aphrodite was born in Petra tou Romiou from the sea, they wanted to say figuratively this is how Cyprus was born. Aphrodite is also known as Kyprida.

Eratosthenes said Cyprus was rich in vegetation. It was overgrown due Troodos. Troodos as i indicated above is a piece of oceanic crust. Today, if we want to study the oceanic crust must make a borehole from the ocean bottom at a depth of six kilometers to get rocks. This is not necessary, since the same rocks found in Troodos. That is why it is great importance of Troodos. Cyprus is continuing and so far every year to grow.
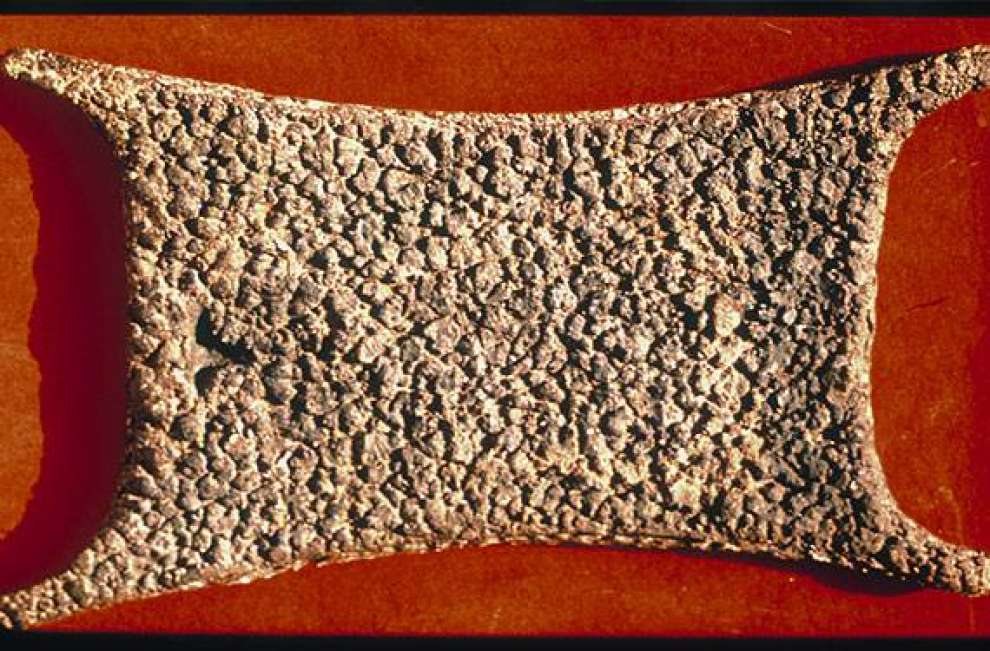
In the pictures below you will see some pictures of rocks with many holes. This rocks once were under the sea.

 English
English
 Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Русский
Русский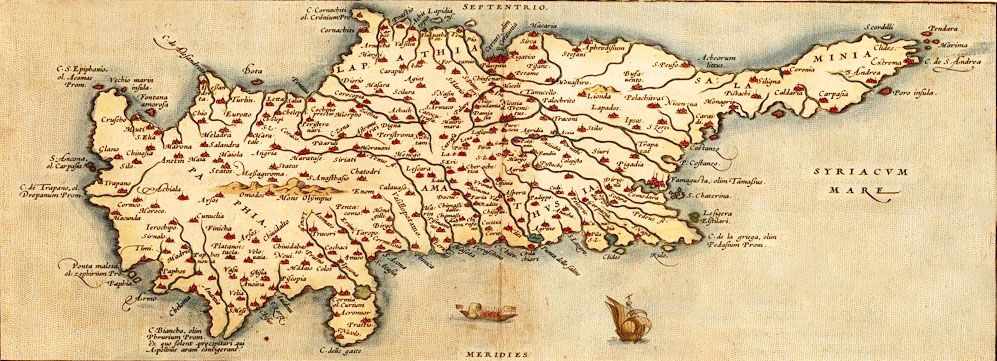










 Posted by
Christina Nicolaou
Posted by
Christina Nicolaou






